In order to deliver a flawless product to customers, software testing is a technique performed by software development organisations to assess the quality of the programme. To design the product, the needs of the customers and their recommendations are explored. The items must be supplied to the clients after adequate validation and verification, which lessens the burden on the firms after the products are released.
Introduction to Current Trends
The current trend in software testing that better meets industry demands is the growth of dependability models. Since verification and validation are carried out by distinct people in a typical testing procedure, efficient automation offers a stronger link between the two than does that approach. These automated processes are necessary for real-time applications since they form the core of unified testing, which also includes manual testing.
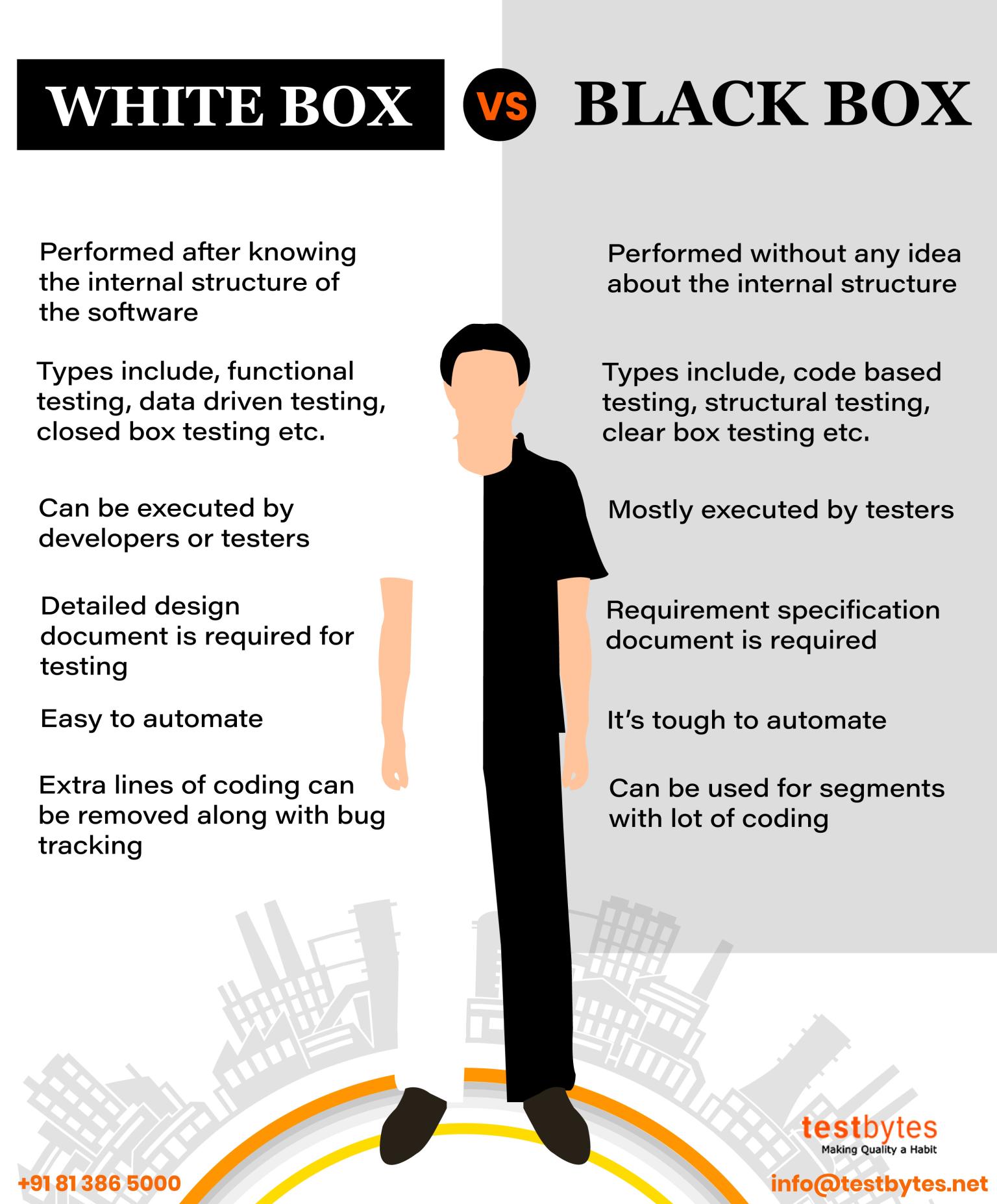
The technique of manual testing is used to examine the system design and find problems based on test cases. It takes a testing developer with the necessary understanding to complete this repetitious procedure. An automated testing environment is created with multiple levels of abstraction under various domains and a wide variety of diversity rules in order to eliminate the problems with manual testing. Industry-wide automated testing’s overarching goal is to speed up computations and cut costs.
Concept required to grow the Business
Many businesses still use outdated test automation techniques that have negative effects, such as the inability to automate useful tests, produce and maintain automated tests at the lowest possible cost, or promptly identify errors. Such unfavourable consequences prevent businesses from gaining the benefits of test automation they anticipate, use up resources for software development, and potentially jeopardise software quality. “Increasing immature test automation processes with poor effects” is referred to as “improving test automation maturity” in the software industry and research community.
Although there have been more initiatives in the software industry to promote test automation maturity, not all of these efforts have been successful. According to a recent poll on software testing practises, around 65% of the almost 2000 software businesses worldwide sought to increase test automation maturity, but only about half said their efforts were successful. To develop test automation maturity effectively, the industry requires the guidelines.
Software testing, which is based on standard verification over static and dynamic environments, aids in improving product design. In a static environment, verification is carried out using formal processes and methods, but in a dynamic environment, verification is carried out at any level using test cases. Dynamic analysis is more effective than static analysis and can spot mistakes in product design.
Early-stage testing decreases product problems by discovering defects and reducing product failure after implementation. Software testing makes use of straightforward tests and code procedures to cut down on mistakes at every level of the programme. When it comes to the verification and validation processes, the selection of the best product is examined in the former, whilst the product’s qualities are examined in the latter. It enables the client or user to examine the programme that has been created and make necessary corrections to meet their demands.
Read Also: How AI will Change the Software Testing
Data on the item or service being evaluated is gathered during the software testing process. Running programmes or apps while testing allows you to find and repair bugs. The process of developing test cases is crucial for getting the most out of the system and spotting as many errors as possible early. Throughout the whole software development process, this is the most economical use of time and resources. Automated testing is unable to carry out comprehensive testing.
Recent work on a novel application using the Intelligent Security and Automation System (ISAS) architecture has revealed that robotic testing dramatically cuts the price and time required for trials, which is crucial for monitoring a project’s development. It is critical to adhere to the evaluation approach in order to construct the best test suites.
Aspects and Objective
The most important stage of any product development is testing. The testing stage serves as the last checkpoint for any rejections or commission errors. Testing computer programmes is a little more challenging than practising a framework to make sure it functions as intended. When in doubt, it is critical to keep in mind that each inquiry, audit, survey, or walkabout is a test. If there have been more successful static testing attempts, there will be less problems with dynamic testing. IT has frequently demonstrated that the incremental cost of resolving an issue decreases with the speed with which it is identified and fixed. The process of testing starts with the representation of an item. All evolutionary algorithms yield results that are close to those of the Genetic Algorithm. When exposed to a certain set of environmental circumstances, tests are done to make sure that a product or service satisfies specified requirements.
There are two aspects to this objective. The main objective of this fragment is to confirm the accuracy of the requirements point of interest for the item. The settings and code are excellent fits for every criterion, as shown in the second part. For a job to be deemed exact, all affirmation requirements must be satisfied.
Read Also: What is Cloud Testing? Why is Cloud Testing Important
Problems in software test automation
The following actions are mainly responsible for problems in software test automation:
Unfounded hopes for automated testing
It goes without saying that test automation has several advantages. Most significantly, it saves time, energy, and resources for the QA team. Does this not imply that increasing the number of procedures that are automated would increase efficiency? Not exactly. People’s unrealistic test automation expectations can ruin the entire testing process.
Manual testing is important. Manual testing should never be disregarded. In certain cases, manual testing of an application is far superior to developing automated test scripts.
Manual testing is appropriate for:
- Usability testing for UI
- Quick compatibility testing using, say, one or two devices
- One-off tests
- Ad-hoc analysis
- Testing for both localization (L10N) and internationalisation (I18N).
There are still manual testing components. Those who support automated test scripts are necessary. Therefore, even if you insist on automating as much of your testing as possible, there will still be manual tasks to complete.
- Solution: A well-defined testing plan.
Using inappropriate tools
If the proper tools are not used, test automation will not be efficient. With so many testing options available, it is simple to become misled. The poor tool selection might lead to scalability issues in addition to the failure to achieve your initial test automation goals.
- Solution: Make judicious tool selections.
Automate pointless tests while ignoring crucial test cases
Unfortunately, QA teams frequently begin the automation process by arbitrarily automating test cases. They now have an excessive number of pointless tests and little test coverage. Additionally, by using this method, you run the danger of not include all pertinent cases and having poor software quality.
- Solution: Determine what is worth automating.
Incorrect testing window
Many teams still consider testing to be something that happens after development. QAs begin their work only when the entire build has been completed. This antiquated method cannot ensure excellent software quality. It does not allow QAs to adequately test all levels, and there is typically not much time left for testing.
- Solution: Run automated tests concurrently with development.
Inadequate testing
This is the most difficult of the test automation difficulties. A lack of appropriate testing arises when QAs depend too heavily on automation and focus on passing tests rather than detecting issues. The problem is that automation creates a false sense of security. It is tempting to limit human interaction and accountability for the outcomes when automated tests run regularly. Such an approach has disastrous consequences, such as poor test design and inconsistent and inefficient testing.
- Solution: Training for the QA staff.
Improving test automation using genetic algorithm
Software should be tested once it has been created. A study by NIST indicates that software flaws have a significant negative impact. As a result, the test stage of software development is one of the most delicate stages and accounts for around 50% of the total cost. The cost of software testing has been greatly reduced by the introduction of automated software testing tools since it uses a lot of resources but does not offer any new functionality to the product. Various techniques for automatic software testing have been developed over the past ten years with the goal of maximising error detection while generating the fewest amount of test input data possible.
One of the algorithms that has been extensively employed in the area of test data creation automation is the genetic algorithm. Traditional genetic algorithms are effective at producing useful test sets, but they take a long time. Applying prior knowledge to the issue or including a local search phase in the evolutionary cycle can help to some extent. Chromosomes do not attempt to enhance themselves; instead, they only wait for a mutation or recombination to haphazardly improve them. This is a notable flaw in the genetic algorithm. Additionally, the genetic algorithm treats each segment of a chromosome as a whole and does not distinguish between its many sub-sections. Due of this, a genetic search is extremely comparable to a blind search.
The advantages of genetic algorithms are as follows:
- They exhibit an unpredictable pattern that can be statistically assessed but cannot be precisely predicted (i.e., stochastic).
- Another area where it thrives is big data. It works well with probabilistic and non-deterministic rules.
- It’s an excellent tool for simultaneously optimising several objectives. This method has certain shortcomings.
- It can take a lot of time, use a lot of computer resources, and be difficult to create objective functions.
Improving test automation using AI
Automation of the testing procedure and quality control results in considerable time and resource savings. However, there are a few things to think about when using AI and machine learning for test automation. We go through the six factors to take into account when using artificial intelligence and machine learning for test automation.
1. Visual evaluation testing (UI)
Software engineers do visual testing as part of their quality control procedures. They assess if the application functions and appears as intended for the user. Understanding the sorts of patterns that machine learning can detect is crucial. Manual inspectors are better able to spot imperfections, whether they are noticeable, aesthetic, or functional.
While analysing complicated surface textures and picture quality, a typical machine vision system may need a thorough review. Therefore, visual assessment of online or mobile apps is better suited for a deep learning tool or system.
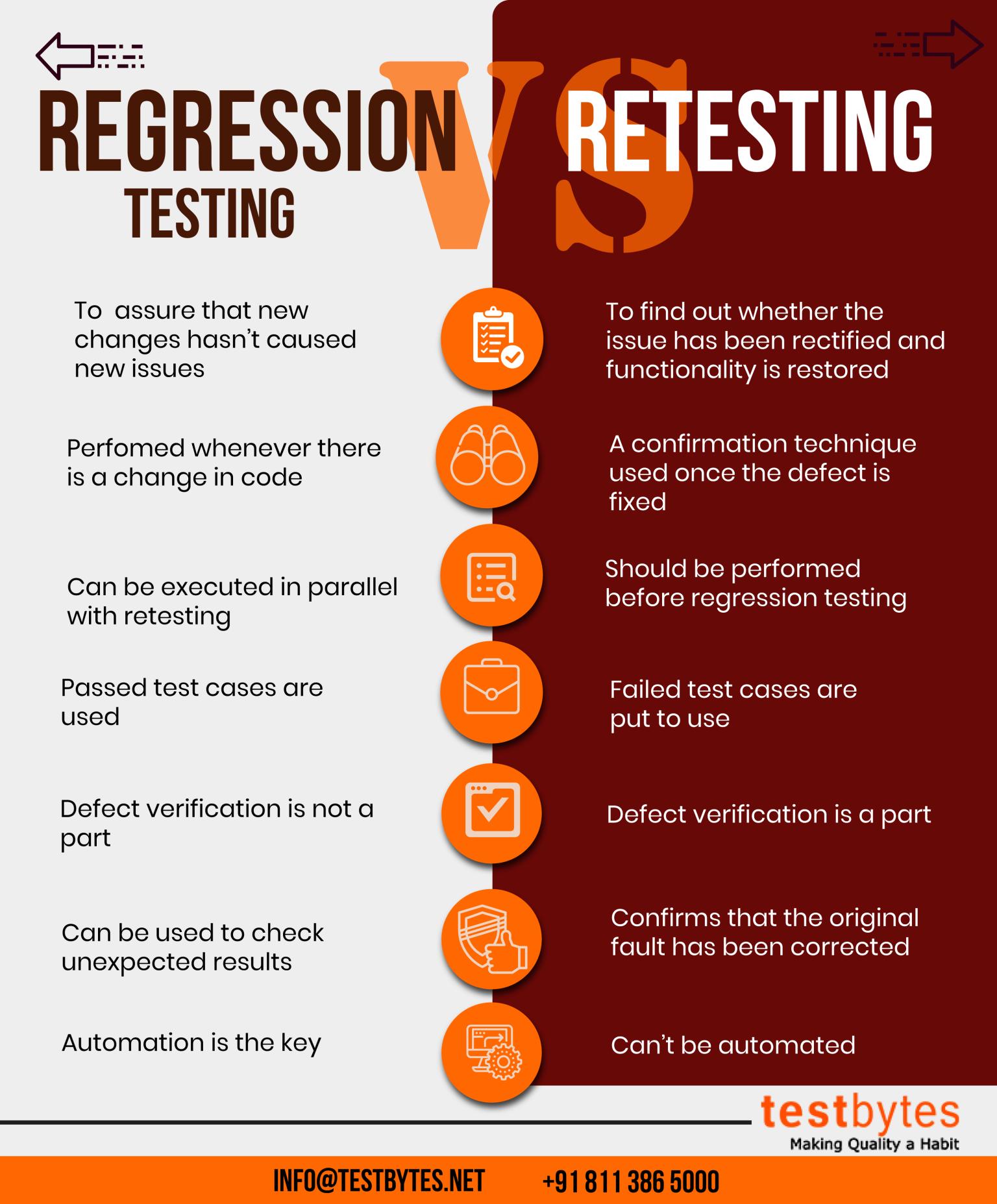
Read Also: A Study Towards Regression Testing Techniques and Tools
It delivers quick and precise outcomes. Developers can rely on this technology in situations when human intervention might be deemed dangerous. Developers may eliminate manual testing and immediately find visual issues by implementing a quick machine learning test.
2. API Testing
Software testing of the Application Programming Interface (API) allows data flow and communication between two software systems. The benefit of API testing is that it is more accurate than UI testing at identifying application flaws. When the test fails, it is simpler to examine the source code. It can withstand application modification, which facilitates automation.
To get thorough test coverage while testing at the API level, you require a greater level of technical know-how and equipment. Additionally, software testers need to be knowledgeable in their respective fields. It is crucial to take into account if testers have a thorough understanding of various application interfaces.
AI allows you to transform manual UI testing into automated API tests that handle all the labor-intensive tasks. You will be able to connect the actions taken in UI tests to API tests as a novice.
3. Domain expertise
In software testing, domain knowledge is essential. With artificial intelligence, you can test apps more effectively whether they are subjected to human or automated testing. For instance, developing test scripts in Java, Python, or C# might be difficult. Advanced testing technologies allow the creation of test scripts and codes by testers. AI enables robots to self-write faultless code.
Manual testing is preferable to handle complicated test scenarios, though. You would be able to determine when to execute test cases using manual or automated testing if you had sufficient domain expertise. Knowing how the application will function and help the company is crucial when implementing AI in test automation. We should typically anticipate failure in results while executing test automation. No matter how little, important, or serious the application fault is, it must be easy for QA teams to scale it.
4. AI Spidering
Writing test scripts for test automation is most frequently done via spidering. It contains a feature that allows you to use AI/ML technologies to direct users to your web application. The application then automatically starts to crawl over itself while scanning and gathering data.
As you perform tests, the tools gradually assemble a dataset and develop patterns for your application. When you use this tool again, it will identify possible problems by referring to its collection of patterns and behaviour.
Though some of the distinctions might not be relevant, keep that in mind. In this instance, a subject matter expert will need to confirm whether the problem that ML has identified is a bug or not.
Understanding which components of an application should be evaluated will be made easier by spidering AI. Simply said, machine learning will handle difficult jobs, and a tester will need to confirm the accuracy of the output.
5. Test Scripts
When a code has been changed, it will be challenging for software testers to estimate how many tests are necessary. Artificial intelligence-based automated testing solutions can determine if a given application needs numerous tests or not.
The use of AI in testing has two advantages. You can save extra time by ceasing to run tests that are not necessary. It is practical to evaluate a system’s overall performance without running the test scripts again. As a result, you don’t need to manually check on it every time.
6. Automated Tests by Robots (RPA)
RPA is the name given to software that automates repetitive commercial tasks without involving any human beings. It assists in fully maintaining and automating the interfaces already present in IT systems. RPA scans the screen, uses the systems to traverse, then locates and collects data.
The tests may be run via online, desktop, or mobile apps, and the duties are entirely handled by the bots. It assists with test data setup and regression test execution.
RPA testing initiatives are undoubtedly being taken by many businesses. However, business testing is powered by RPA, which may reduce the amount of testing that testers complete. Scalability, codeless testing, cost savings, higher productivity, precise findings, and adaptability are among RPA’s key benefits.
Artificial intelligence can automate about half of the test procedures. Machine learning may be used by testers to train systems to find mistakes that manual testing might miss. You may speed up the process of getting reliable findings by incorporating AI into your test automation. Since AI handles the majority of the testing procedure, you can save time.
Automation has a significant impact on the software industry’s ability to increase test efficiency. Projects use extra people for manual testing or utilise automation tools or techniques to increase the amount of test automation in order to ensure test coverage satisfaction and hence lower risk. The option relies on whether the project cycle time or test time is reduced. The significance and necessity of automating software testing have grown as a result of rising software usage, increasingly complicated software functionalities, and shorter timeframes for evaluating programme quality. By applying machine learning to automate software testing, mistakes in manual testing are reduced and assessment is sped up.
Because it helps software testing companies to boost their test efficiency, automation is essential in the software business. In order to assess created software with a range of drawbacks, a number of automated approaches have been conceived to provide test data, approaches based on genetic algorithms being one of them.




















![11 Differences Between iOS and Android App Testing [Infographic]](https://wp.testbytes.net/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/info-ftr-img-1-1.png)