Artificial Intelligence (AI): Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the latest technology to be leveraged across all industries and domains which are increasingly complex and continuously accessible marketplace, organizations must evolve. It is the ability of machines to perform tasks that usually require human intelligence.
How does Artificial Intelligence work?
- AI works by merging big data sets with iterative processing algorithms and with intelligence to learn from features and patterns in the dataset that AI systems Analyze.
- Each time an AI system performs a data cycle, it checks and measures its performance and gains additional knowledge.
- AI science aims to create computer systems that can simulate human behaviour to solve complex problems using human-like thought processes.
- AI systems use different technologies and different methods and processes to achieve this goal.

AI helps to access and manage the computing resources to train, test, and deploy AI algorithms and is playing a essential role in the software industry which also includes software testing. Testing is the basic activity aimed at detecting and solving technical issues in the software source code and assessing the overall product usability, performance, security, and compatibility. It’s not only the main part of quality assurance; it is also an integral part of the software development process.
Since AI has the ability of mimicking human intelligence, the penetration of AI in testing is on the rise.
Evolution of AI in Software Testing
According to the World Quality Report 2019-2020, it is stated that AI-based testing is on the rise, and to make testing smarter, more effective, and more efficient, organizations are adopting AI-based tooling and processes in software testing. Typically, the application of AI in software testing will make the entire testing process faster, clearer, easier, and budgeted. Therefore, AI-based testing will provide a strategic platform where software testers can leverage AI and take the testing process to a new level and thus deliver more quality results to businesses.
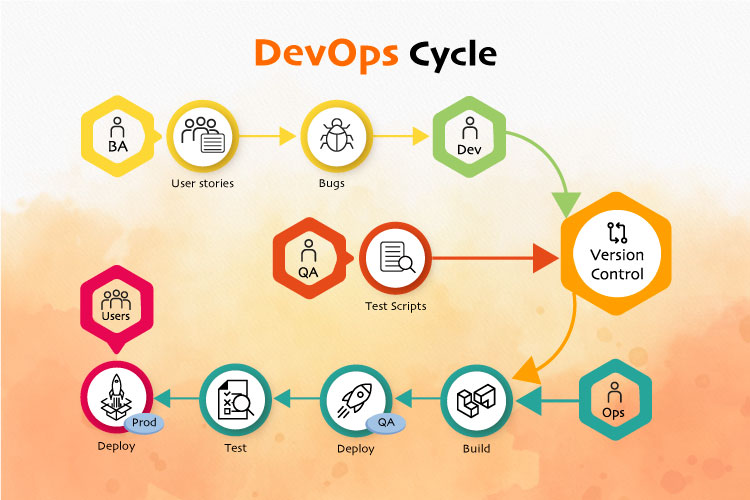
The paradigm of software testing has evolved significantly over the past two decades. Right from manual testing to automation testing, where selenium is considered to be one of the finest test automation tools, the testing journey has been quite encouraging. However, in today’s fast-paced IT world, the domain of software testing has to come up with innovative and well-researched testing methodologies.
AI algorithms can completely mimic human intelligence, and ML allows computers to learn automatically without any human intervention. Interestingly, AI and ML involve the development of unique and specific algorithms that can access data learn from that data by extracting patterns to make decisions, and these predictions are to be used in software testing effectively.
Benefits of AI in Software Testing

1. Reduced Test Flakiness
By automating repetitive tasks and using algorithms to detect bugs and issues, AI helps to speed up the testing process and improve the accuracy of results. This means all the software can be tested more efficiently and effectively, saving time and resources while ensuring a higher-quality product.
2. Better Test Coverage
Artificial intelligence has the potential to automate manual tests and identify issues quickly, reducing the time required to detect bugs and errors. By automating testing activities and reducing human error, AI can help you deliver better quality software more quickly.
3. Faster Feedback Time
AI helps in faster detection of bugs in the product. Early detection results in improved product quality since the developers receive faster feedback about the product. Accelerated feedback time also improves developer productivity since issues are reported at a faster pace. The impact of AI-based testing multiplies by a huge margin when the tests are run in Continuous Integration pipeline.
4. Faster Test Script Generation
Codeless AI testing is significantly faster than either manual testing or traditional automated solutions, as testers save time generating code. This allows companies to increase their ability to run tests and deploy more quickly.
What is AI-based Testing?
AI-based testing is a software testing technique in which AI and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms are used to effectively test a software product.
Machine learning is one of the key techniques we use to achieve this. It forms the basis for many AI systems, but not all. AI and machine learning in software testing deliver better and more effective automation, relieving teams of the burden of repeating and refining testing.
Many software testing methods are now powered by Artificial Intelligence .The objective of AI-based testing is to make the testing process smarter and highly effective. With the inclusion of AI and ML in testing, logical reasoning and problem-solving methods can be applied to improve the overall testing process.
Moreover, enterprises are rushing towards tools that can leverage AI and ML algorithms and can be used for testing the software effectively. It has also been seen that businesses get many benefits from AI-based testing as it will enable faster and continuous testing, complete automation without any human intervention.
Some of the benefits of leveraging AI in software testing:
1. Visual validation:–
It helps to make sure that all the visual elements are engaging and can function properly. Improved accuracy: with the advent of AI in automation testing, repetitive tasks are handled more effectively and the results are recorded more accurately. AI has pattern recognition and image recognition capabilities that together help to detect visual bugs by performing visual testing on applications. It helps to make sure that all the visual elements are engaging and can function properly.
2. Improved accuracy:–
Through machine learning, AI helps to generate test data where testers can feed the data into an AI machine allowing it to perform various tests at every stage without the need for manual testing hence improving the reliability and security of the software.
In the manual testing method, the chances of human-prone errors are high, especially in situations of repetitive tasks. Automation testing helps in removing these human-prone errors. Thus, AI helps in removing the minute chances of errors and improves the overall accuracy of tests.
3. Better test coverage:–
AI in testing increases the test coverage as it can check the file contents, data tables, memories, and internal program states seamlessly. Saves time, money, and efforts: Software tests need to be repeated whenever there is an instance of change being made in the source code. AI in testing increases the test coverage as it can check the file contents, data tables, memories, and internal program states seamlessly. It also helps to determine if the program works as expected and delivers effective test coverage.
4. Saves time, money, and efforts:-
Software tests need to be repeated whenever there is an instance of change being made in the source code. Manually this becomes time-consuming and takes a lot of effort from testers. But, with AI-driven tests, repetitive tasks are handled properly, quickly, and efficiently.
5. Faster time-to-market:–
AI uses a set of algorithms to analyze software functions and identify errors through automated testing, thus minimizing the headaches of repetitive software testing tasks (such as regression tests), improving accuracy, and accordingly shortening time to market. AI-driven tests support continuous testing, and thus products are released faster which helps businesses go early-to-market.
6. Reduces defects:–
AI-driven tests support continuous testing, and thus products are released faster which helps businesses go early-to-market. AI in testing helps in early and fast bug identification, which ultimately reduces the defects and makes the product bug-free, and reliable for end-users.
What are the 4 main categories of AI-driven testing tools?
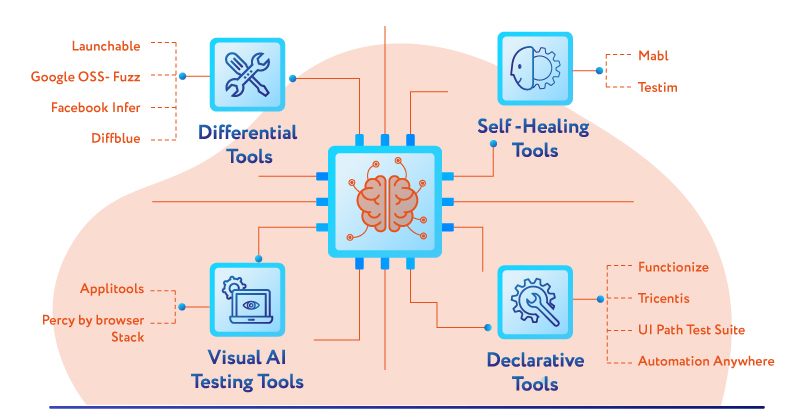
1. Differential tools:-
Helps test different versions of similar applications. Carries out a comparison to understand differences, versions overbuilds and learn from classification feedback. Visual: Image-based testing needs visual validation. Differences are classified and application versions over each build are compared in this type of testing.
Tools leveraging AI and ML algorithms aim to proactively and automatically identify code quality issues, regressions, security vulnerabilities, and more. This is done through code scanning, unit test automated creations, and more. If your team lacks skills to address the above objectives or does not have the time to continuously address these tasks, consider some of these options. The outcome will be faster releases, improved quality through fewer escaped defects, and better productivity for developers. Some of the tools under this category are:
Launchable is based on an ML algorithm that predicts the likelihood of failure for each test based on past runs and whenever the source code changes under test. This tool lets the user record the test suite so that tests that are likely to fail are run first. One can choose this tool to run a dynamic subset of tests that are likely to fail, thereby reducing a long-running test suite to a few minutes.
It looks at code automatically upon a code pull request and performs a kind of code impact analysis that adapts to the recent code changes. It then selects only the most relevant subset of your regression suite to save time to approve the code changes and integrate them into the pipeline.
It is a fuzz testing tool that aims to make common open-source software more secure, stable, and reliable. This tool combines modern fuzzing techniques with scalable and distributed execution. This tool supports C/C++, Rust, Go, and Python code.
Facebook’s Infer project also enables better code quality through its AI algorithm. The AI engine from Facebook can automatically find null pointer exceptions, memory leaks, concurrency race conditions, and more in Android and Java code. Similarly, it can also find the same issues together with wrong coding conventions or unavailable APIs in C, C++, and iOS/Objective C code.
DiffBlue connects into your source control repository (Git, Perforce, etc.) and creates a base line of unit testing automatically through AI. Once a regression is found, a flag will be thrown reporting the issue. The motivation for DiffBlue to create their solution was mostly to improve code quality by helping developers who do not like to own test creation.
2. Visual AI testing tools
Visual testing is a software testing technique in which the look and feel of an application is tested by leveraging image-based learning and screen comparisons. With pattern and image recognition capabilities together, it helps detect visual bugs to test the look and feel of an application.
Visual AI testing tools address the pain of constant changes made to the UI (user Interface) layer together with an ever-growing number of platforms, screen sizes, and configurations that make testing coverage a nightmare for test engineers and developers. With the ever-growing number of platforms that vary in screen sizes and have different configurations, it has become a tedious task for test engineers and developers to effectively test the UI layer.
Also, the UI layer experiences constant changes from time-to-time as businesses wish to provide a better user experience. Therefore, today there is a dire need for visual AI testing tools that effectively test all variations of these UI layers.
Some AI/ML tools that fall into this category are:
1. Applitools:
This is an AI-powered visual testing and monitoring platform. This has been named a next-generation test automation platform powered by Visual AI. The major features include Applitools Eyes which helps to increase test coverage and reduce maintenance. The Ultrafast grid helps with cross-browser and cross-device testing and accelerates functional and visual testing by 30 times. This Applitools platform integrates with all modern test frameworks and works with many existing testing tools like Selenium, Appium, Cypress, etc.
2. Percy by BrowserStack:
It is an all-in-one visual review platform that comes with amazing features such as pixel-by-pixel diffs, responsive diffs, and snapshot stabilization. This tool allows cross-browser rendering, high-speed rendering, and has parallelization capabilities. Percy helps teams automate visual testing. This Browserstack tool is used to typically capture screenshots and compare them against the baselines and display visual changes. It increases the visual coverage and helps teams to deploy code changes with confidence.
3. Declarative tools
Declarative tools have different use cases from the others but still aim to enhance test automation productivity and stability. Declarative tools that leverage ML and AI have significant abilities related to NLP, DSL, RPA, and MBTA methods. The common ground between the methods is to eliminate tedious, error-prone, repetitive actions through smart automation. While in this category we list RPA, this specific method is not solely around automation of testing, but also around automation of processes and tasks done manually.
These tools aim to enhance test automation productivity and stability. These tools leverage AI and ML and have significant abilities related to Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Natural Language Processing (NLP), Model-based Test Automation (MBTA), and Autonomous Testing Methods (AT). The main aim of these methods is to eliminate tedious, error-prone, repetitive tasks through smart automation. Some of the tools that fall under this category are:
Focusing on declarative testing, we can take as an example tools like:
- Functionize
- Tricentis
- UIPath Test Suite
- Automation Anywhere
1. Functionize:
Especially Functionize, specify leveraging NLP to create test automation scripts without any coding skills or development languages.
The major benefits of this tool type are as follows
Fast test automation creation.
No coding skills are required. Faster maintenance of test automation scenarios.
2. Tricentis:
This is an AI-driven, next-gen automation testing tool that allows Agile and DevOps teams to rapidly achieve test automation goals. It allows teams to go beyond continuous testing with AI. It allows automating end-to-end testing of software applications. This tool combines multiple aspects of software testing (test case design, test automation, test data design and generation, and analytics) to test GUIs and APIs from a business perspective.
3. UiPath Test Suite:
This is the latest Test Suite that can be used to automate and centralize the testing process and helps to launch resilient robots and ensures high-quality of every automation. The UiPath Test Suite consists of UiPath Studio Pro, UiPath Test Manager, and UiPath Orchestrator. Thus, UiPath test Suite can be used to automate tests in UiPath Studio Pro with drag and drop interfaces, helps to manage tests with UiPath Test Manager, and also helps to execute tests witn UiPath Orchestrator. Therefore, UiPath Test Suite is helping businesses with a 360 degree testing and is helping RPA developers to build more, test better, and fix never.
4. Automation Anywhere:
These types of tools should solve problems for the right persona depending on the skillset available.
4. Self-healing tools
Apply AI to testing to identify when a function has changed. Then, the test can automatically update itself to be relevant and not fail during execution. Element selection in tests is auto-corrected when the UI changes.
Code-based test automation is by nature less stable. It requires tuning constantly per platform or environment, and its entire foundation is the application objects. These objects tend to either change every few weeks, or worst case they are used inefficiently (e.g. XPATH vs. Object ID, etc.).
Some of the tools are as simple as a web browser plugin installation (Mabl, Testim). Some tools that assist in test maintenance with machine learning are richer in their abilities and are integrated into an end-to-end continuous testing solution (Perfecto, Tricentis).
At the heart of these tools there is a ML algorithm that upon each execution and in between them “learns” the website and/or application under test. It scores the element locators from each screen in the app based on reliability and probability to be found successfully.
Code-based test automation is by nature less stable. It requires tuning constantly per platform or environment, and its entire foundation is the application objects. These objects tend to either change every few weeks, or worst case they are used inefficiently (e.g. XPATH vs. Object ID, etc.).
In automation tests, the problem of flakiness, reliability, and maintenance issues persist, and this is one of the main reasons why AI and ML have been introduced in test automation. To overcome these problems, self-healing tools have been developed that are mostly based on a record and playback mechanism, wherein the main ML engine resides in the self-healing of the recorded scripts. Some of the tools that fall under this category are:
- Mabl:
It is the leading intelligent test automation platform built for CI/CD. Mabl crawls your app screens and begins to run default tests that are common for most applications. It also uses ML algorithms to improve test execution and defect detection.
- Testim:
This tool uses AI and ML algorithms to automate testing to its full extent. AI is used to speed up the authoring, execution, and maintenance of the tests. Testim includes self-maintenance of automated tests that are ML-based. This results in the fast authoring of stable automated tests.
Best Practices for Testing AI Applications:
Assess Information Technology infrastructure
Successful execution of an AI strategy requires discipline and the best practices listed here. Responses may also contribute to adoption. Consider the use of resources in terms of the time, cost, complexity, and skill set required to build an AI model and demonstrate a business case.
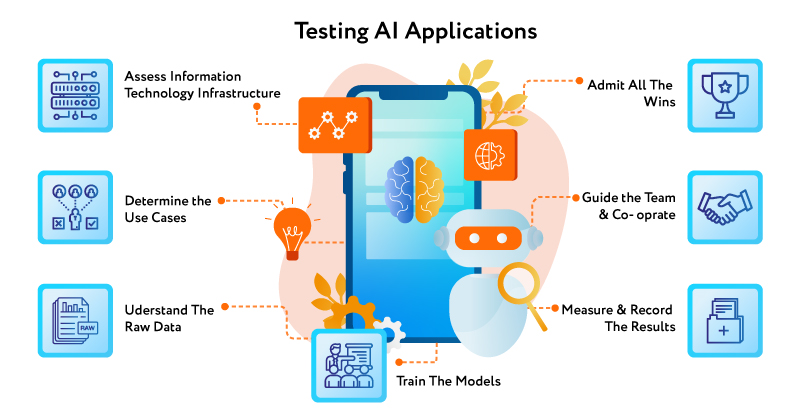
Determine the use cases
Determine how the peers and competitors have strongly deployed AI platforms. Look for suppliers with a solid track record to mitigate risk. They talk to stakeholders about the utilization cases and the benefits of implementing AI.
Also, use AI accelerators from popular cloud service providers (CSPs), which may already be included in BPM (Business Process Management), RPA (Robotic Process Management), DMS (Document Management System), and iPaas (Integration Platform as a Services) platforms. Working with stakeholders and educating them on how to use AI solutions increases their likelihood of use and drives adoption across the organization.
Search for relevant use cases for the optimized deployment of artificial intelligence in each of the following areas:
- Machine learning (ML)
- Natural language processing (NLP)
- Natural language understanding (NLU)
- Optical character recognition (OCR)
- Chatbots
Learn how your competitors and peers have successfully deployed AI platforms. Look for vendors with a reliable track record to reduce risk. Consult with stakeholders on your use cases and the advantages of implementing AI. Also, leverage AI accelerators from prominent cloud service providers (CSPs) that may already be included within your LCAP, DMS, BPM, RPA, and iPaaS platforms. By working with your stakeholders and teaching them how to use your AI solution, the more likely they are to use it, driving organization-wide adoption.
Understand the Raw Data
Insufficient data may lead to misrepresented results and AI implementation failure. If you can comprehend the raw data, garner your business experts’ assistance to access a detailed interpretation. Comb through the data to ensure there aren’t any typos, missing components, skewed labels, and other errors. Ensure your data samples contain every element you need to analyze. Incomplete data may cause misleading represented results and AI execution failure. Ensure that the sample data contains all the elements required for analysis.
Losing focus on the raw data can lead to skewed results and loss of confidence on the machine learning models. If you do not understand the data, get help from business experts to gain a full understanding of the story the raw data is telling you. Analyze it to ensure that there are no missing values, incorrect labels, or typos and check that the sample contains the full spectrum of all users that you wish to analyze.
Also, consider the relationship between data labels and values that you are trying to predict based on dependent data and ensure that there is no biased data (data favoring a particular result). While analyzing the raw data, you will get an understanding of the limitations of your data set and model. This will help you communicate the scope and limitations of your predictions based on the pattern of the data to your stakeholders.
Train the models
You will need high-quality historical data to train your ML models. Use AutoML engines to build image, speech, video, and natural language, recognition models. With AutoML engines, any user can upload their images and automatically create an ML model using a drag-and-drop interface. Essentially, it imports data, tags the data, and trains the model. The best part is that an AutoML engine manages all the complicated work for you.
Training an ML model requires high-quality historical data. Generate natural language recognition, image, video, and speech using the Auto Machine Learning engine (AutoML). The AutoML engine allows users to upload images and automatically generate ML models using a drag-and-drop interface. Import the data, label the data and train the model. The best part is that the AutoML engine takes care of all the hard work.
Measure and record the results
You should experiment with artificial intelligence, but you should also incorporate disciplined tracking, monitoring, and measurement at every step using a critical approach. Also, it’s essential to continually audit your deployment to ensure it consistently aligns with your business objectives. Changing your strategy is more effective than accepting failure.
Continue testing your models and predictions to drive further improvements where necessary. Keep your data clean, and retain a master raw data set to use for every testing round. You can also use your master data set to test modified use cases. Monitor your model for potential risks and issues. Don’t forget to add time for managing any unexpected problems. While performing AI tests, one should also incorporate measurement, precise tracking, and monitoring using a complex approach throughout the action.
Also, it is essential to continuously check the deployment to ensure it is frequently coordinated with the business objectives.
Guide the team and cooperate
Artificial intelligence continues to get better, but it still requires the correct data. The issue is it’s difficult to find data science experts. Therefore, invest in continuing education for your stakeholders. Add to your training initiatives by creating an environment where collaboration is part of the culture. A crucial factor for AI implementation success is change management.
Create short-term and long-term objectives of what you expect to achieve using predictive analytics and then machine learning and then natural language processing and on down the AI list. Map out how each deployment affects each business line and how it enhances your employee workflows AI continues to improve, but it still needs relevant data. The problem is that it is difficult to find data science experts. Therefore, invest in further participatory education.
Admit all the wins
Celebrate every win, and involve every executive and stakeholder. Try to complete your projects within or before 12 weeks to encourage continued engagement. As you learn from each successful project, you can scale AI across more business lines and company locations. Use your goals as success benchmarks, and focus on your results. When focusing on the outcome, keep in mind that AI platforms can take structured and unstructured data sets.
Finally, using best practices for implementing AI requires a long-term perspective. Remember that AI deployment is a marathon and not a spring. Understand what AI is currently capable of executing, and be realistic about your timelines and your expectations.

Conclusion:-
A better understanding of the differences between AI and human intelligence is needed to better prepare for the future in which AI will have the most profound effect on our lives. With the advent of AI in software testing, businesses are now able to achieve faster tests and reliable products. Leverage next-gen AI-based testing services by next-gen testing services provider to get faster and quality releases with more efficiency and accuracy.
There are best practices for implementing AI in companies like Assessing IT infrastructure, determining the use cases, understanding the data, training, and measuring the records. An AI application needs to be tested for functionality and system levels. It is similar to testing of traditional software in aspects of test planning, test modelling, test design, and execution. Testing of an AI system becomes more challenging and function test quality evaluation becomes an integral part of AI application testing.