Traditional Software testing requires costly and dedicated infrastructure and sources.
Software is growing in complexity which makes it very tough and pricey to build and preserve testing facilities that imitate actual-existence environments in-house.
The maximum consistent issue in software services and products is evolution. This evolution is mainly due to new technologies and person/patron necessities; one such technology is Cloud Computing aka cloud testing.
In cloud testing, Cloud computing environments are used to simulate an actual global state of affairs.
Cloud refers to software programs checking out the usage of assets from the cloud infrastructure this is acquired on-call at a reasonable cost due to the pay-according-to-use nature of cloud computing.
It does not shop facts on private computer systems. It gives on-call the availability of PC offerings like servers, data storage, networking, databases, and so on.
What is cloud computing?
The “cloud” has been used as a metaphor for the Internet browser and an Internet connection Cloud computing is on-demand access, through the net, to computing resources—programs, servers facts Storage, improvement tools, networking skills,
Cloud computing is a way of leveraging the Internet to consume software or other IT offerings on call. Users’ percentage processing electricity, Storage space, bandwidth, reminiscence, and software.
Users will pay as they pass and handiest use what they need at any given time, preserving the price to the consumer. Cloud computing is a business model as well.
Instead of buying and installing the physical infrastructure essential to run software packages, Cloud computing gives a streamlined, simplified strategy to this complexity and the capital expenditure it necessitates.
Cloud computing models.
There are 3 models of Cloud Services:
Saas: Software as a service is a cloud version that provides programs over the internet as a carrier.
Users no longer to install and hold the software on their devices, they can get access to it through the net, rather than managing the software and hardware with the aid themselves.
It is likewise called a Web-based software program, hosted software.
It runs on SaaS service provider servers and manages software applications, inclusive of security, availability, and overall performance.
Paas: Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud model in which hardware and software assets are provided to users over the net by a third-party supplier.
These resources are required for application development. A PaaS service provider hosts the hardware and software on its infrastructure and developers install hardware and software to run new software applications freely.
Iaas: Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is a cloud version that provides digital computing sources over the net. A user can get a very new digital system with the desired configurations and the use of IAAS without spending an extra price.
Types of Cloud
- A public cloud is a service provided by a cloud computing service provider to most people. These services can be availed by any person who desires to use them; all they need to do is pay for the offering’s services.
- Private cloud, this the infrastructures are provided for the different use of an organization. The company can be the proprietor of the infrastructure, or a 3rd party might also own them.
- Community cloud, the infrastructures are given for using a particular group of users from organizations that represent the specific community.
- A hybrid cloud is the combination of the above model.
What is Cloud Testing?
Cloud testing means software testing by the resources from the cloud infrastructure. In this kind of testing, the software program to be examined takes the benefit of cloud infrastructure and technology to simulate an actual global scenario.
Cloud computing has affected all components of the software program existence cycle, including software testing.
Testing as a Service (TaaS) is terminology like SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS in cloud computing. it consists of the usage of the cloud and testing of the cloud.
TaaS is a model in which testing activities are purchased or hired on the customer’s demand from the third party which has all the testing resources for a real-world environment.
This model gains more recognition when technology and customers’ requirements become more complex, and the need for high-quality, error-free, easy-to-use, and flexible software arises.
TaaS has aloof the problem of installing and maintaining the test environment and sourcing of test assistance.
This helps to reduce the costs of software production. Almost all software testing can be completed e on the cloud
Why do you need Cloud testing/ benefits of cloud testing?
- Cloud testing has become very critical in software program development these days, and the need to perform testing as a service (TaaS) can’t be overemphasized.
- In conventional software testing, the company desires to have the hardware and software program for testing, and it is very high priced to hold the hardware and software program and also to resume their license.
- Cloud technology brings support using presenting a way to check the software in a completely challenging and dynamic environment the use of the pay-as-you-use feature of the cloud, cuts the fee of software production.
- Virtualization, a vital function of cloud generation gives a manner to check software programs in one-of-a-kind surroundings like extraordinary working structures, configuration, and systems.
- Using cloud testing helps to improve the performance of software program testing by way of decreasing the time to construct the test environment.
Cloud Testing tools.
SOASTA: CloudTest is a production overall performance testing device for Web packages. It can simulate thousands of virtual public cloud infrastructure services.
ITKO LISA: This product is designed to improve the effectiveness of the software program development teams, especially the ones concerned with cloud computing and custom applications
LOADSTORM: This is a tool that is straightforward and much less high-priced. It is used for load checking out of internet-primarily based and mobile applications.
BLAZE METER: This tool is utilized in measuring load checking out and peer-to-peer overall performance of cellular applications, websites, and application programming interfaces.
iGATE PATNI: Two businesses, iGATE and Patni, got into an alliance and gave delivery to one of India’s largest IT businesses, iGATE Patni. This organization also provides a TaaS solution, which is a cloud-based framework for dynamically scalable and occasional-fee take-look at automation.
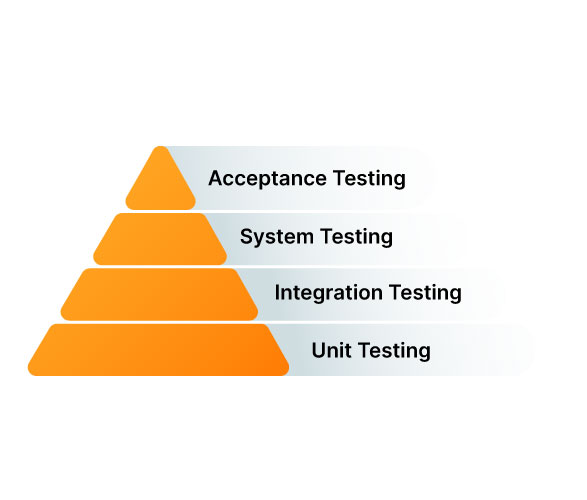
Types of testing that can be performed in cloud testing:
Functional testing is a high-quality warranty check that deals with all of the consumer necessities, affords the capacity to ensure the system works as anticipated, and gives each developer and user a guarantee that the product meets client requirements.
Functional testing of the Internet and non-internet-based programs can be accomplished in the cloud.
NON-FUNCTIONAL TESTING
This testing is also referred to as the performance testing technique; it’s miles executed to make certain that the utility meets the overall performance expectation of the user.
The scope of nonfunctional requirement testing is broader in cloud testing than in conventional testing.
The maximum essential element of performance testing is to investigate the software’s firmness and scalability.
Pace determines whether or not the application responds speedily; firmness determines whether or not the software remains equal under changing conditions and scalability, which determines the best consumer load a system can manage.
Stress checking out and cargo trying out is each variety of performance testing.
Cloud Testing Vs Conventional Testing
| Parameters | Cloud Testing | Conventional Testing |
| Definition | Cloud Testing is one form of software testing wherein the software program packages are examined by way of using cloud computing services. | Conventional testing is a sort of testing in which software is examined primarily based on pre-defined testing standards in line with the exceptional management machine to maintain standards. |
| Test Environment | Cloud testing offers test surroundings-based applications as well as on-user and utilization of applications to test as per custom requirements and satisfaction. | Conventional testing has a pre-described environment for checking out any software. This testing was performed in a check lab with restrained assets. |
| Cost of Testing | The cost of testing in cloud testing is much less compared to conventional testing as there is no need to maintain physical infrastructure for testing. Users and clients handiest pay what they use. | The cost of testing in conventional is better as we need to hold physical infrastructures and software as nicely required for trying out. |
Benefits of Cloud Testing.
- Availability of Mandatory testing environment: In cloud testing, the client’s environment can be effortlessly reflected for effective testing without making an investment in the extra hardware and software program resources for testing.
- Less costly: Cloud testing is extra cost-efficient than conventional types of testing. Customers, and the testing team, pay for the simplest of what they have used.
- Quicker testing: It is quicker than the traditional method of testing as corporal infrastructure management for testing is removed.
- Scalability: Cloud computing assets may be expanded and decreased every time required, based on the demands.
- Customization: Cloud testing may be custom-designed in keeping with the usage, price, and time primarily based on the style of users and user surroundings.
- Tragedy regaining: It can be done without difficulty viable as the statistics backup is taken on the cloud vendors as well as at the user’s stop.
Challenges of Testing in the Cloud
Performing Testing periodically
Performing Testing Periodically Test labs in agencies commonly sit idle for a longer duration, consuming capital, electricity, and real property.
Just about 50% of the infrastructure earmarked for testing is underutilized.
As cloud computing is a common environment wherein a single Server with a couple of CPUs, RAM, and SAN or NAS garage are divided among many users via digital hosts or IP addresses. All users in a cloud computing environment are in the end accessing a physical system.
Therefore, at a time if any person is the usage of the assets intensely then it can create overall performance issues for the alternative customers at the same time.
So, the performance testing results from the team may vary on occasion depending on the load of the cloud environment. This is one of the tests demanding situations in a cloud environment
Data migration
Migration of information from one cloud carrier company to another turns into a tough project understanding the different database schema requires plenty of time.
Integration Concerns:
A distributed application offers many special servers which might be on a web page or off-web site.
In the cloud environs, the dispensed application will deal with many specific digital machines which will be onsite or offsite and there will be response time challenges in the integration of these virtual machines.
The company simply orders the digital machines on the cloud without knowing their bodily locations. However, if machines are placed at a long distance, then latency troubles can occur frequently.
Testing of all components
Performing cloud testing calls for testing all the components associated with an application that needs to be tested just like the server, garage, and network, and also validating them in all layers.
Qualitative Services
Business is frequently concerned with the migration of their critical packages to the cloud environment.
They have the principle situation approximately service availability, scalability, flexibility, and continuity.
Critical commercial enterprise packages are enterprise touchy and can incur a big loss to the agency both in terms of popularity and money if the carrier-level agreements with the patron aren’t met effectively.
Therefore, the cloud computing environment desires to offer demonstrated take a look at outcomes in terms of service availability, scalability, flexibility, and continuity.
Functional Testing aspects
The business application running on the cloud computing surroundings is needed to bypass the behavioral elements of the utility in conjunction with system testing, acceptability testing, integration testing, and interoperability testing.
All of those tests must have been completed before any employer ought to flow its business-crucial application to the cloud computing surroundings.
The testing surroundings ought to resemble the actual cloud environs to obtain the high-fidelity test results.
Operational challenges
Obscure from technical challenges, there are a pair of operational challenges as follows.
Lack of Standardization
There’s a loss of widespread solutions to integrate the general public cloud with inside data centers. there’s an absence of interoperability.
Hence, it’s miles tougher to switch carriers if the office desires to.
Security Concerns in the Public Cloud
Data within the cloud is also stored in a remote location that will lie outside the company’s legal reach.
Privacy and Data Security in Cloud packages are multi-tenant in nature, owing to the same the threat of unauthorized data access cannot be ruled out.
The tester has to confirm that there’s no leakage of data while testing the business application over the net in a cloud environment.
Data inside the cloud may be stored in an exceedingly faraway location that would lie out of doors the company’s legal attain.
The tester desires to ensure that there is also no leakage of data at the same time as testing the commercial enterprise application in a cloud environment.
Usage
Because there are just a few options accessible, improper utilization may occasionally result in expense increases for newer firms. To encourage cost efficiency, businesses should thoroughly assess their demands before choosing a cloud vendor.
Planning
The assembly, use, and disassembly of the environment should be carefully planned by the project teams and test teams.
To reap the utmost benefits of Cloud, the usage has got to be planned properly.
Performance
As cloud infrastructure is shared, there are also scenarios where performance dips.
There could also be planned downtimes/maintenance windows on the cloud vendor side which might impact performance too
Accessibility and Recovery Testing
The Other challenges that the testing team could countenance are as follows.
Application data replication testing should be tested with the help of a third-party vendor as replication is not under the control of the tester in the case of the cloud environment.
Lastly, the tester needs to deliver their due diligence to procure accurate test results which should be comparable to the physical server environments.
Environment Configuration
for cloud testing, it becomes hard to manipulate the infrastructures like servers, storage, and so forth. Deployment and testing consequently, lead to troubles.
Use of Multiple-Cloud Models: It will become hard to manage more than one cloud at a time which can lead to complications, security, and synchronization issues.
Upgradation in Cloud: The biggest assignment of cloud testing is to do up-gradation in the cloud and ensure it does not affect the prevailing users and data.
Conclusion
Hope you like the article about what is cloud testing. Traditional software testing is great, but the cloud makes work faster and easier.
However, relying on the cloud all the time is not a wise decision as well. It’s your requirement that should define the technology.