Imagine that you have launched or even revamped a website that has been your business forefront for a long time. Obviously there will be concern and anxiousness. But to make sure that the change works there is a process in existence. The name of the process is Split testing!
What is Split Testing?
The process allows you to compare various versions of websites to test which version offers a better conversion rate. In split testing, the page traffic is randomly distributed over various versions of the website.
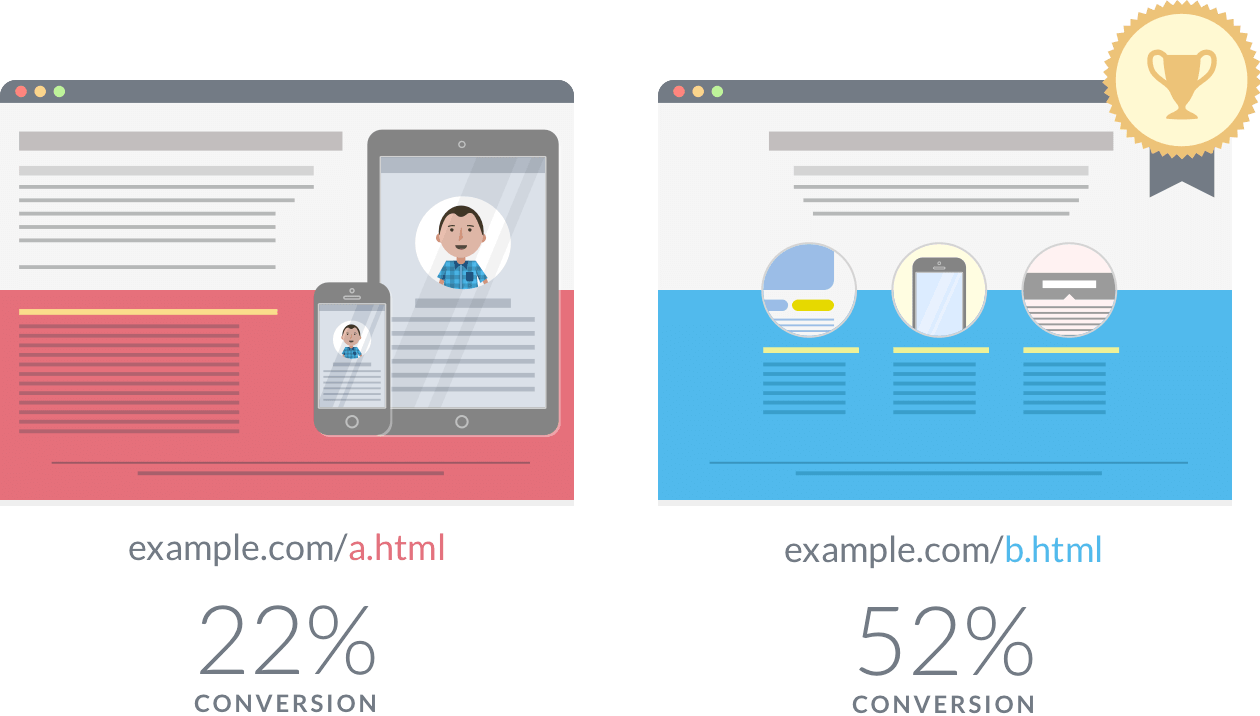
The software used for the purpose tracks and analyze the performance of each of these versions to recognize which converts the maximum visitors to the leads. Split testing will find the version with the maximum conversion rate.
Need For Split Testing
The process provides qualitative feedback about the user’s experience of your website. It helps you identify the barriers that are stopping the conversion of your visitors into the leads.
The process gives you a report on which version of your website the conversion rate is highest and with which version do your users interact the most.

Why You Have to Choose Split Testing For Your Website?
- It can be performed on any website: Split testing is not confined to any specific types of websites and can be executed for all types of websites.
- Increased ROI: If you choose the correct A/B testing tool, split testing will not cost you high and will give you better returns. It helps you select the best version of your website, which will give you better conversion rates, hence the higher average order value and hence the greater turnover.
- It is Easy: Not that complicated to execute, you can easily execute split testing to get desired results.
- It is most suited for low-traffic sites: split testing is the only method to test the website conversion rate for low-traffic sites. It is also easy to distribute the traffic and analyze the results when the traffic is low.
How to Pick the Best Split Testing Tool?
A good tool not only performs testing but also analyses results and proposes steps to get better results.
A good tool should include all the necessary features like:
- Data Insight: A good tool should offer data insights to recognize the customer journey.
- Marketing Campaigns: It proposes a marketing campaign to improve your website marketing.
- Usability: The tool should be easy to use.
- Personalized experience: It should provide a personalized experience to reach the right audience.
Top 5 Split Testing Tool
Now when you the features of the good split testing tool, here we have for you a few of the best split testing tools. You can use any of these tools to identify the best website version for you.
- Google Optimize: Being a Google product, there is no second thought on its capabilities. It is integrated with Google analytics for added advantage. It supports MVt and has an editor for both code and images.
- Oracle Maxymiser: For more sophisticated campaigns, Oracle Maxymiser is the right choice. It offers a personalized experience and helps you target the exact user. The visual editor makes it easy to use and to create your rules directly. It provides a good analytics report.
- Convert Experiment: It is easy to use the tool, with a live chat feature to assist you in your queries. It is integrated with Google analytics for better analytics.
- Apptimize: If you have a responsive website design, then Apptimize is the best tool for your purpose. It supports mostly all coding languages
- Adobe Target: Supported by Adobe marketing cloud, this tool is the best choice for enterprise based websites that can support a distinct test team. This tool supports real-time changes to the website.
How to Do Split Testing?
You should know the test factor and testing scenarios that are important to test. Usually, split testing is conducted when there are major changes to the website.
- Relaunch of your website: you can get better results with less code implementation using CMS. It is very beneficial for websites and web pages where major changes take place.
- Back-end heavy tests: The process can execute easily on websites and web pages with back-end heavy tests. It helps in the immediate and successful deployment of variation without any additional by developers.
- Page copy length: Though short-form copy is better, it is on split testing to decide which is better after all things are data-driven and let data decide the actual scenarios.
- Page copy position: positioning your content on pages is very important, but there are no fixed rules as to which position is best and will give you the best results, so let split testing do its work.
- Sign up workflows: When you validate two versions of sign up processes, it is good to run the test. As it requires the implementation of less code and also enhances the overall performance.
Step by Step Methodology For Split Testing
You have to follow a systematized approach to execute the process. the steps you can follow are:
Step 1: Analyse Website Data
As a start, begin with website data. Deploy any website analytics tool to analyze your website data and its weak points. It will help you to find the right approach and prioritize your split testing.
Step 2: Create a Hypothesis
Split testing is never based on your personal opinion; it is driven by facts and data analysis. Make a hypothesis on which you want your testing to be based, you will later know on what basis the results are based on. A strong hypothesis will also help you know your specific goals.
Step 3: Test Your Hypothesis
Since now you have your hypothesis ready, create a new version based on it and test it against the original page.
Step 4: Make data-driven decision
Based on the results, decide which version of your website offered you better results. Your decision should be based upon the data obtained from the test.
5 Factors For Successful Split Testing
A few tips that you should follow to have successful split testing:
- Choose the right one: There are two types
- A/B testing
- Multivariate testing (MVT)
A/B testing compares two versions where only one variable is different, while MVT can test multiple variables at a time. Depending upon your requirement and hypothesis choose the better option for your split testing.
- It’s not a one-time process: Many companies test for split testing once and are satisfied with its results, but for growing your business you should continue to split test your website, to get better traffic and conversion rate on your website.
- Make a correct hypothesis: Deciding upon which factor you want to test upon is a very crucial task. Don’t just randomly pick any testing variable, spend some time and use an analytical tool to decide the correct test variable.
- Track the correct information: Always be assured of the deciding factor while execution. The split test focuses on that factor only. If your aim is to attain a larger number of people reading your blogs, then make it your deciding factor and track it while you conduct split testing.
- Focus on both short term and long term results: It is important to focus on both short term and long term results to get a deep insight into split test results.
5 Important Fields that You Should Consider While Split Testing
Following fields play an important role in building your online presence.
- Headlines: It is important to test headlines while performing split testing. Headlines are the deciding factor for the visitors to decide whether to stay or leave the page.
- Offers and promotions: People are generally attracted by offers and promotions and they play a great role in lead conversion. The way you exhibit offers and promotions play a great role in capturing the users. So split test various ways to exhibit the offers and analyze their results.
- Calls to Action: They are the communicating link between the users and the web page. Their placement, color, size, text, etc. should be properly verified in the test.
- Colour: Colours have a great psychological effect on users; always test the usage of colors to get better returns.
- Online advertising: Online advertising on various platforms like Google, Facebook, Instagram, etc. play a great role in marketing. Use tools like Google Analytics or Facebook analytics to validate your advertisements.
Who Should Implement Split Testing?
- Virtual Business Coaching Businesses
- E-commerce Businesses
- Digital Marketing Companies
- Software Companies
Difference Between Split testing and A/B testing
|
Split testing |
A/B Testing |
| Control version is compared with entirely different version of a website | Control version is compared with websites that has small changes |
| It’s better to use split testing when there are major changes | Can be used to optimize the existing page |
| Can be used to find out one design direction is better than the other | Can be used to test one variation of a variable and that too even on a single page |
Conclusion
In the scenario where the world is dependent on the web for all its needs and it has become the most popular platform to get access to your requirements, you need to build your reputation to get ahead of your competitors.

Getting ahead based on your assumptions is not a right and long-lasting method. You need to get hold of some more reliable ways to assure your success.
And split testing is one reliable method to get more visitors and leads. To assure that you carry out split testing for your websites and web pages.